Spring Data JPA
Java Persistence API
JPA 是一种 Java 规范,定义了如何在 Java 对象和关系型数据库之间进行数据映射和管理(CRUD)。
JPA 使用 SQL 来进行数据库操作:当使用 JPA 进行数据访问时,JPA 实现(例如 Hibernate)会自动生成并执行 SQL 语句。例如,当调用 repository.save() 方法保存实体时,JPA 会自动生成相应的 INSERT SQL 语句来插入数据。
ORM: Object Relational Mapping
Hibernate 是 JPA 的一种实现, Spring Data JPA基于Hibernate
ORM 将编程语言中的对象(例如 Java 对象)映射到数据库表,每个对象的属性对应于数据库表中的字段。例如,一个 Student 类的实例可以对应于数据库中的一行记录。
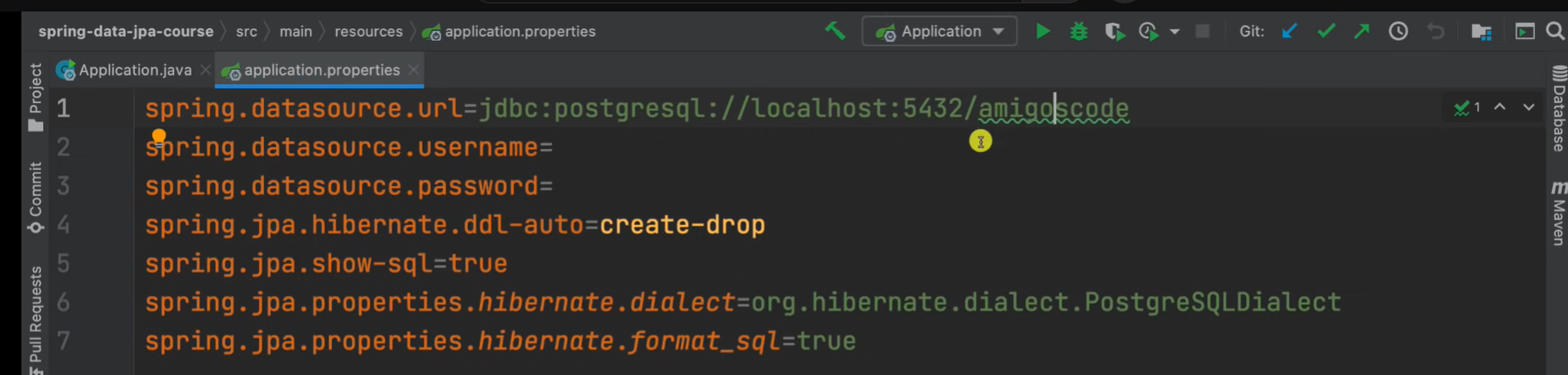
1. config application.properties, start the application
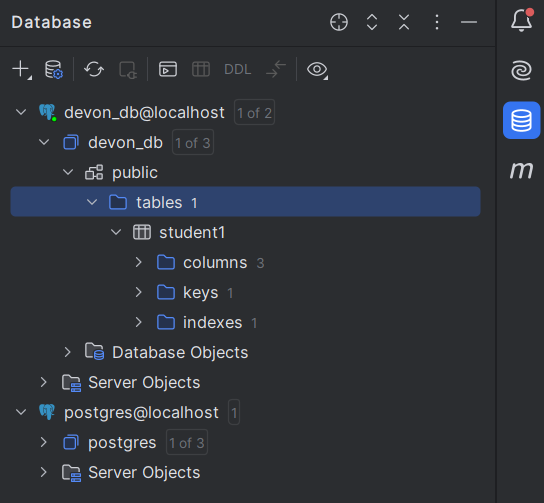
2. connect to db
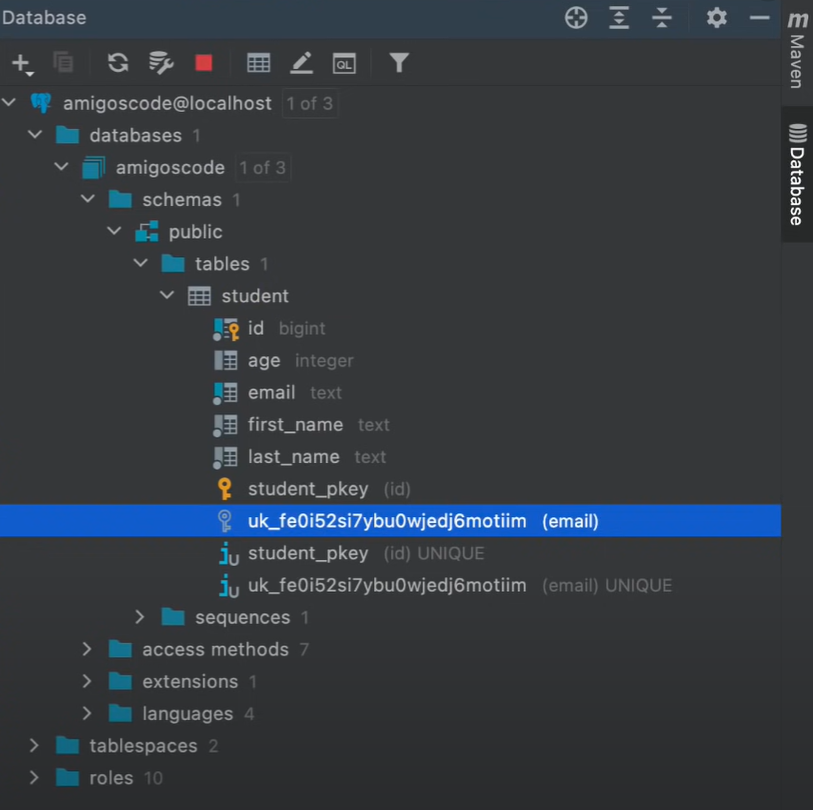
3. Define a Class and map it to db
4. CRUD: Extends Repositories
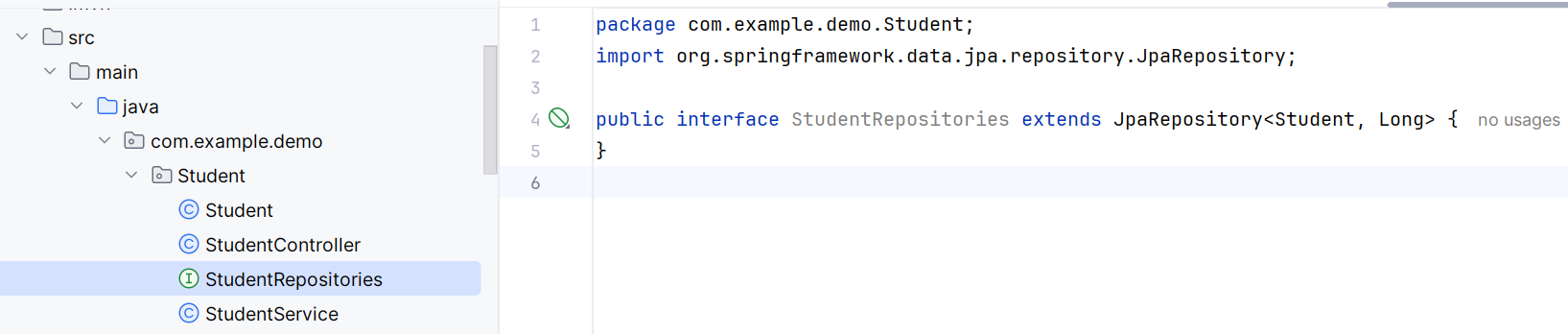
Repositories server as the Data Access Layer
Sequence是和Table平级的数据对象
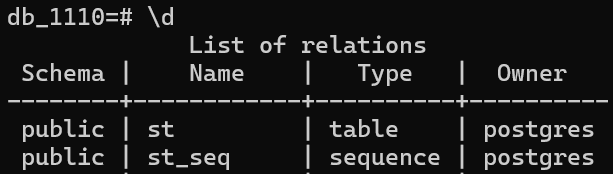
Table
@Entity(name = "ST")
public class Student {
Attributes:
@Id
@SequenceGenerator(name = "st_seq_generator", sequenceName = "st_seq", allocationSize = 1)
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.SEQUENCE, generator = "st_seq_generator")private Long id;
@Column(name = "email", updatable = false, columnDefinition = "TEXT", unique = true)private String email;
}
| Aspect | Table-level Constraint | Field Attribute |
| Scope | Entire table, often involving multiple columns | Single column |
| Main Purpose | Defines relationships between columns (e.g., multi-column uniqueness) and table integrity | Defines storage characteristics of a column, such as type, length, uniqueness, etc. |
| Defined in | Typically defined in the @Table annotation in JPA | Typically defined in the @Column annotation in JPA |
| Typical Examples | @UniqueConstraint, @ForeignKey, etc. | nullable, unique, length, etc. |
| Applicable Scenarios | When constraints involving multiple columns or foreign keys are needed | When defining column-specific properties, like allowing null values, uniqueness, length, etc. |
11/11
SEQUENCE是在什么时候发挥作用的?是在插入数据的时候不用指明id吗?
Yes, you can delete this.id = xxx in constructor. No need to specify this attribute manually.